Blog

AR and VR are reshaping the defense industry. Global militaries are investing heavily into these sectors. In this article we will take a look at some key ways in which these technologies can be used and the countries deploying them.
In this article we will explore how AR and VR are transforming the defense industy and how militaries worldwide are using these technologies.
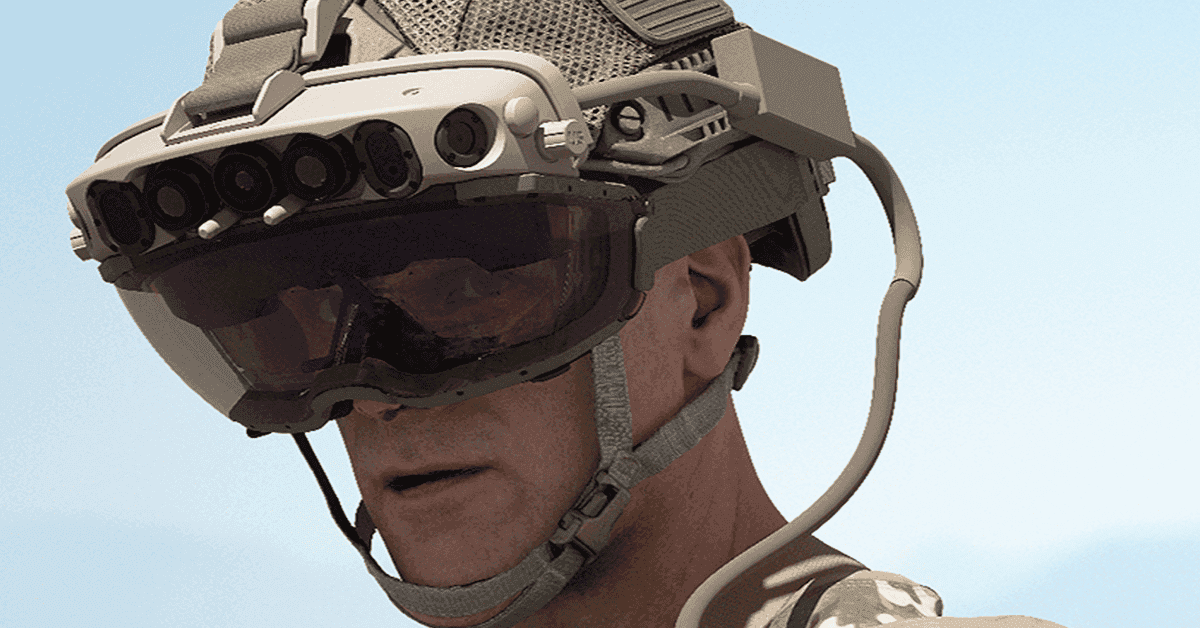

Table of contents
Introduction
Key Areas
Global Adoption and Use Cases
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
AR and VR are reshaping the defense industry
Militaries all over the world use AR and VR
The 4 key areas are VR training, AR overlays, Strategic Planning and FPV Drones
China and the US are leading in the adoption of these technologies.
AR and VR: The Future of Military Innovation
From strategy rooms to the frontlines, technology is reshaping warfare at an unprecedented pace. The next revolution in the military industry isn’t about weapons—it’s about how we train, plan, and fight. Technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are poised to redefine combat and strategy, making operations more efficient and safer for soldiers.
In this article, we will dive deep into the ways in which these technologies can be used as well as how militaries are implementing these into their processes.
This article is an extension of our youtube video about the same topic, which you can watch here.
If you would like to learn more about the industry or similar topics, check out our articles on VR military training or the top VR in aersopace.
Use cases of AR/VR - Why AR and VR Matter in Modern Warfare?
The military has historically driven technological innovation, from the compass to satellite communications. Today, AR and VR are emerging as critical tools for modern warfare, enhancing human capabilities and ensuring safety on the battlefield. As military recruitment faces challenges, technologies that preserve soldier lives and increase mission success are more valuable than ever.
AR and VR applications in military operations focus on:
Training: Immersive simulations replicate real-world scenarios, improving preparedness.
Remote Machinery/Drone Operation - AR and VR are used to remotely operate machinery and drones.
Combat Enhancements: Real-time AR overlays and VR-operated drones provide critical information.
Strategic Planning: Detailed VR environments enable more effective decision-making.
AR and VR in Training: Preparing Soldiers for the Unexpected
One of the most established uses of VR in the military is for training. Simulations allow soldiers to learn by doing, without the risks of live exercises. For example, during a U.S. Army exercise in Fort Bragg, VR scenarios were employed to replicate urban combat situations, enabling soldiers to practice tactical maneuvers in a high-stress, yet controlled environment. Similarly, the UK’s Royal Navy implemented VR training modules for sailors to handle warship navigation under simulated storm conditions, improving their preparedness for real-world maritime challenges.
Studies underscore the effectiveness of VR training:An HTC study found that 80% of military trainers observed increased confidence among soldiers after VR exercises.
Chinese military personnel reported a 97% satisfaction rate with their VR training experiences.
Emerging use cases also include multi-national joint drills, where soldiers from allied countries train together in VR environments, ensuring seamless collaboration and coordination during actual operations.Here are some of the most popular examples of VR training:
Virtual Squad Training Simulations (VSTS): Entire squads train together in VR, using simulated weapons to practice teamwork and tactical maneuvers.
Tactical Combat Casualty Care: Soldiers practice administering first aid under battlefield conditions, building muscle memory for high-pressure scenarios.
PTSD Treatment: VR therapies help soldiers recover from combat trauma by recreating scenarios in controlled environments.
If you would like to know more about these types of VR training, read our article on VR military training.
Remote Machinery/Drone Operation
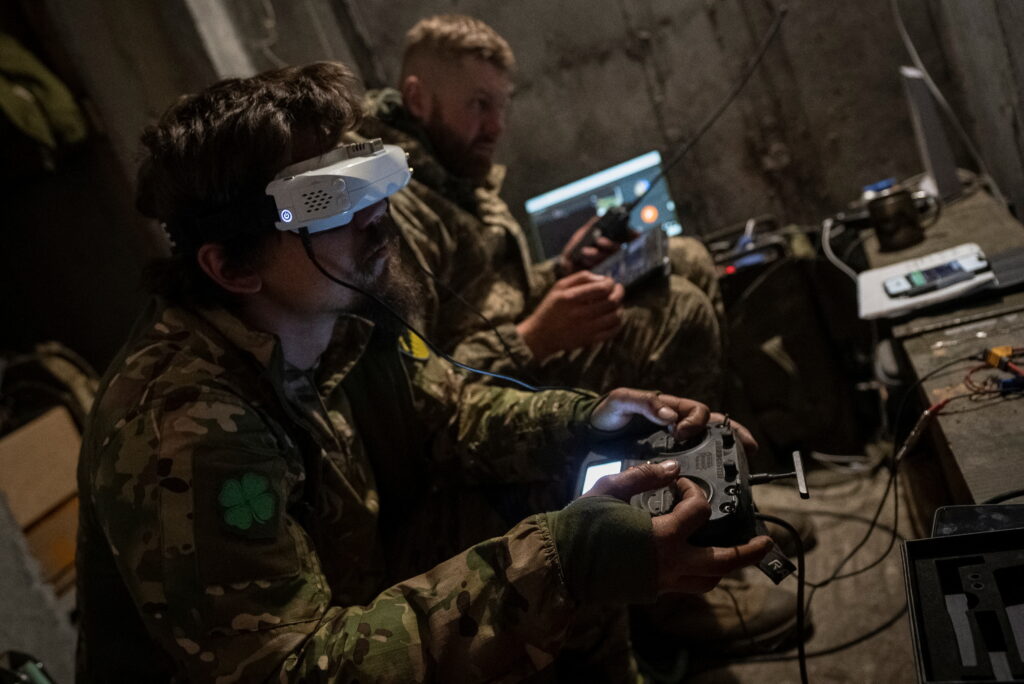
One of the most popular uses of VR right now is in using it to operate FPV drones. FPV stands for “first person view”. With these systems, operators use a VR headset to guide and operate a remote drone which can then be used for surveillance or to attack enemy positions.This has proven incredibly effective on the battlefield in Ukraine, where this has become the go-to way to operate drones.
Apart from drones, VR can be used to operate other vehicles and machinery as well as to maintain and repair them remotely. Apart from the obvious benefit of placing the operators outside of immediate danger, the wider field of view and access to additional digital information is a massive benefit compared to traditional methods of operating machines and vehicles.
AR Heads-up Displays: Enhancing Situational Awareness
AR technology, like heads-up displays (HUDs), overlays critical information directly into a soldier’s line of sight. Recent trials of the U.S. Army’s Integrated Visual Augmentation System (IVAS) revealed significant improvements in soldier efficiency, including faster target acquisition and displaying other useful information to the soldiers wearing these headsets.Similarly, the Israeli military’s Elbit X-Sight helmet has demonstrated success in providing real-time data to helicopter pilots, enabling precise maneuvers and reducing mission risks. These advancements highlight how HUDs are becoming indispensable tools on modern battlefields, enhancing both situational awareness and decision-making under pressure.
These overlays provide real-time updates on ammunition, comrade status, and terrain mapping, ensuring soldiers make informed decisions under pressure. The U.S. military, for instance, has invested heavily in Microsoft’s Hololens to equip soldiers with mixed reality capabilities.
The US military’s implementation of Microsoft HoloLens AR headsets seems to be quite successful as Microsoft is now producing these headsets exclusively for the US military.
AR on the Battlefield: Enhancing Situational Awareness
Beyond combat, VR plays a significant role in planning and analysis. Detailed 3D maps enable military strategists to:Visualize terrain depth for better operational planning.
View troop movements in real-time for analysis and strategy refinement.
Replay operations from various angles
Highlight critical information in 3D space
Such capabilities not only enhance decision-making but also provide insights that were previously unimaginable in traditional planning methods.
Including complex digital twin environments can significantly enhance not only operational planning, but also help the soldiers perform their tasks while the combat is ongoing. This works especially well in combination with AR heads-up displays.

Global Adoption of AR and VR in the Military
AR and VR have already been widely adopted by leading militaries worldwide. In this section, we will take a look at some of the key adopters of this technology. We will look at 4 countries and compare ways in which they have adopted this technology.
These key countries are:
The United States
United Kingdom
Israel
China
United States
The US military has been one of the leaders in the implementation of AR Heads-up displays. This is a great example of a military using an advantageous position of having a strong domestic industry which includes the likes of Microsoft who are able to produce some of the best AR hardware.Apart from AR, the US has deployed a variety of VR training programs across their armed forces. From the Navy to the Air-Force, VR training has been used across all to improve the combat-readiness among soldiers.
Previously, the US has pioneered remote operation of drones. FPV drones which are operated through VR headsets are now one of the most popular and revolutionary technologies changing the landscape of war on battlefields across active zones such as Ukraine.
United Kingdom
The UK has invested heavily into VR training to train soldiers in realistic combat scenarios.As early as 2019, The British Army has invested more than £1 million into immersive training.
The RAF also invested £53 million into advanced simulators to replicate real-life scenarios.
Another example is the Royal Navy, which invested £27 million into a deployment of simulators nationwide that immerses their trainees into a fully virtual world.
Israel
Israel has been one of the leading innovative forces in deploying AR and VR technology across their military.Similar to the US, they have used their innovative military technology industry to lead the way in the adoption of AR technology in defense.
A great example is their Elbit X-sight helmet, which allows the overlay of 3D AI information in AR for helicopter pilots.
In terms of VR training, they have deployed VSTS systems which focus heavily on anti-terrorism action. This is a great example how each country is deploying these technology based on their individual needs.
China
Although accurate analysis on how deeply AR and VR technology has penetrated the Chinese military is difficult, due to the general secrecy of their military, it seems that China is leading the adoption of AR and VR in the military, alongside the US.Chinese universities and research institutions have published a vast amount od studies on the impact of AR and VR on the military and these indicate widespread adoption of VR training and simulators.
Additionally, Chinese soldiers have been seen wearing AR headsets during military drills, idicating that they have started adopting these headsets in their processes.
Conclusion
In the coming decade, we will be seeing a proliferation of AR and VR technologies in militaries across the world.
In some usecases, like FPV drones or training, VR seems to already be the go-to standard. In others, such as AR Heads-up displays, the technology still needs to mature to reach its full potential.
The key challenge for global militaries right now will be to integrate these into cohesive ecosystems that will feed into eachother as the synergy between activations such as VR training, strategic planning and AR HUD’s has incredible potential.
Militaries which manage to implement processes that include these technologies and use cases will unlock immense strategic benefits from these working together.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there something related to this case study on your mind? Take a look at some of the questions we think might interest you!
Can't find the question you are looking for?
Send us a message and we'll get back to you as soon as possible!
Latest
Take a look at our related articles
Send us a message and expect our reply as soon as possible!